Ammonia
Ammonia Assay Kit (AMM)
Method: Glutamate Dehydrogenase Method Liquid reagent, R1: R2=3:1
CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE
For the in vitro quantitative determination of ammonia in serum or plasma. Under normal circumstances, ammonia converts to urea in the liver. With severe liver disease, ammonia cannot be converted and eliminated from the circulation, which in turn causes blood ammonia increase. High blood ammonia is neurotoxic, and will lead hepatic encephalopathy (hepatic coma). Adult plasma ammonia determination mainly use for monitoring and treatment of hepatic com, while also pediatric diagnosis of Reye's syndrome.
PRECISION
|
Inter assay precision |
|||
|
N=5 |
Batch 1 |
Batch 2 |
Batch 3 |
|
Mean(μmol/L) |
122.9 |
121.5 |
117.3 |
|
|
120.57 |
||
|
(Xmax-Xmin)/ |
4.58% |
||
|
Intra assay precision |
||
|
N=20 |
level 1 |
level 2 |
|
Mean(μmol/L) |
122.5 |
439.5 |
|
SD |
2.18 |
2.10 |
|
CV(%) |
1.8% |
0.5% |
Sensitivity
Sample concentration for 330 μmol/L, the change of absorbance should be not less than 0.0100.
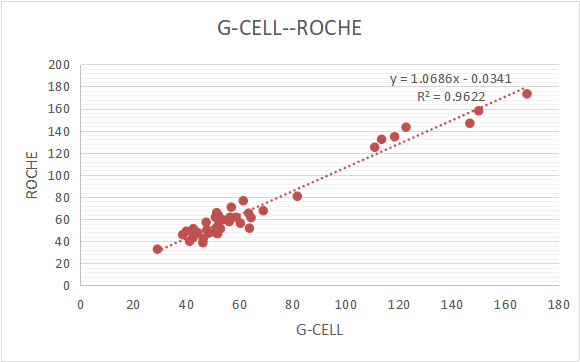
Correlation
The correlation of Roche and Gcell(y) is y= 1.0686x -0.0341,R2=0.9622
Interference
|
Analytes |
Concentration |
|
DB |
50mg/dl |
|
Intralipid |
100mg/dl |
|
Pyruvic acid |
1000mg/dl |
Linearity
Linearity is 20-1000umol/L
