Kappa Light Chain
Method: Immunoturbidimetric Method Liquid reagent, R1: R2=3:1
CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE
There are two types of light chains,kappa and lambda. Each plasma cell synthesizes only one type of heavy chain and only one type of light chain. Heavy and light chains are then assembled to form immunoglobulins. The rest 40% light chains exist in the blood stream as free light chains. Therefore, the free lifght chains can be tested[1]. Under normal conditions, total κ/λ ratio should be normally around 2:1 in serum. In pathological conditions such as monoclonal gammopathies monoclonal immunoglobulin light chains would change the κ/λ ratio. κ/λratio increasing can be seen in rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, acute and chronic hepatitis and cirrhosis, childhood viral encephalitis, primary Sjogren's syndrome, autoimmune diseases, infections, liver disease and kidney disease[1, 2]]. κ/λ ratio decreased can be seen in low immunoglobulinemia.
PRECISION
|
Intra assay precision |
||
|
N=20 |
level 1 |
level 2 |
|
Mean(g/L) |
1.96 |
3.13 |
|
SD |
0.01 |
0.02 |
|
CV(%) |
0.4 |
0.5 |
Sensitivity
|
LOB |
0.01g/L |
|
LOD |
0.05g/L |
|
LOQ |
0.0570g/L |
Interference
|
Analytes |
Concentration |
|
Bilirubin |
60 mg/dl |
|
Hemoglobin |
500 mg/dl |
|
Intralipid |
600 mg/dl |
|
RF |
380IU/ml |
Correlation
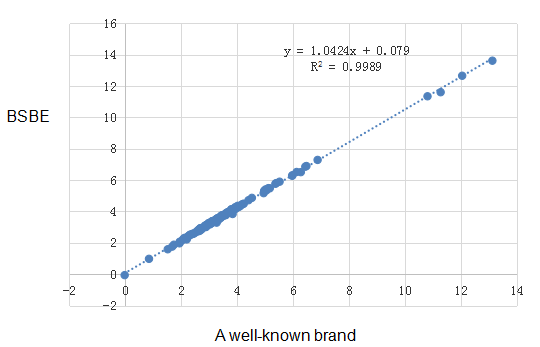
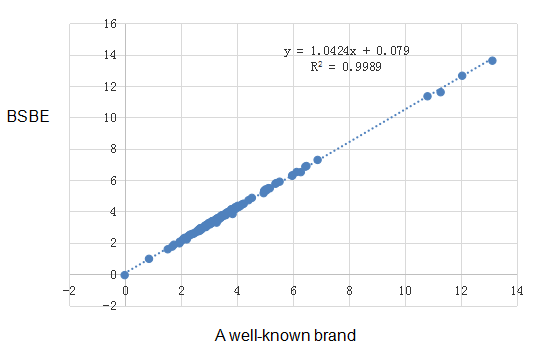
The correlation of a well-known brand(X) and Gcell(Y) is y=1.0424x+0.079 R2=0.9989
LINEARITY
The linearity is [0.50,12.00] g/L.