Haptoglobin
 Beijing Strong Biotechnologies, Inc
Beijing Strong Biotechnologies, Inc
HPT
Haptoglobin Assay Kit
Method: Immunoturbidimetric method Liquid reagent, R1: R2=3:1
CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE
Haptoglobin (HP), also known as binding globin, is an acidic glycoprotein in the serum globulin component, widely exists in human and many mammalian serum and other body fluids, mainly synthesis and degradate in the liver. As one of the acute phase reactive proteins, HP increases in plasma when the acute reaction occur, it also raise up in the case of massive albumin lost caused by burning or nephrotic syndrome. The HAP decreased obviously in intravascular hemolysis such as hemolytic anemia, transfusion reaction and malaria. In addition, the synthesis of HAP decreased in patients with severe liver disease:
(1) Decrease or disappear of haptoglobin: mainly seen in various intravascular hemolytic anemia. Also decreases with liver diseases or infectious mononucleosis.
(2) Increase of haptoglobin: acute or chronic infection, tuberculosis, autoimmune diseases, tumor and taking hormone drugs will lead to haptoglobin increase.
PRECISION
|
Intra assay precision |
|||
|
N=20 |
level 1 |
level 2 |
Level 3 |
|
Mean(g/l) |
0.173 |
1.197 |
2.222 |
|
SD |
0.004 |
0.015 |
0.019 |
|
CV(%) |
2.575 |
1.221 |
0.855 |
Sensitivity
When the sample concentration is 1.03g/L, the absorbance change (ΔA) should be no less than 0.2000.
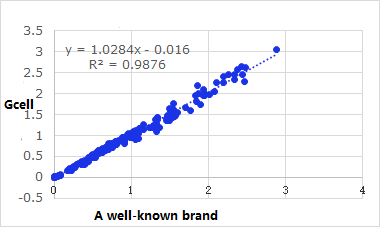
Correlation
The correlation of a well-known brand(X) and Gcell(Y) is y = 1.0284x - 0.016, R2 = 0.9876
Interference
|
Analytes |
Concentration |
|
VC |
50mg/dL |
|
DB |
40mg/dL |
|
intralipid |
0.3% |
Linearity
In the range of [0.3, 2.7] g/L, the linear correlation coefficient (r) shall be no less than 0.990; In the range of [0.3, 1] g/L, the absolute deviation shall be no more than ±0.1 g/L; In the range of [1.0,2.7]g/L, the relative deviation shall be no more than ±10%.