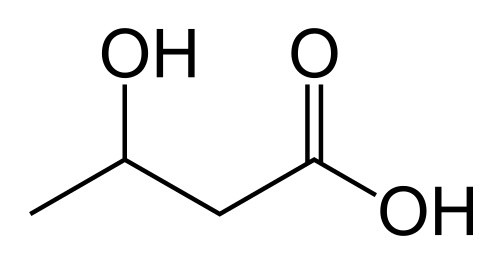
β-hydroxybutyrate
 Beijing Strong Biotechnologies, Inc
Beijing Strong Biotechnologies, Inc
β-Hb
β-hydroxybutyrate Assay Kit
Method: β-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase Liquid reagent, R1: R2=3:1
CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE
Ketosis is a common feature in acutely ill patients. In subjects suffering from starvation, acute alcohol abuse, or diabetes mellitus ketosis can result in severe life threatening metabolic acidosis. The presence and degree of ketosis can be determined by measuring blood levels of D-3-Hydroxybutyrate. Ordinarily, D-3-Hydroxybutyrate is the ketoacid present in the greatest amount in serum. It accounts for approximately 75% of the ketone bodies which also contain acetoacetate and acetone. During periods of ketosis, D-3-Hydroxybutyrate increases even more that the other two ketoacids, acetoacetate and acetone, and has been shown to be a better index of ketoacidosis including the detection of subclinical ketosis. In diabetics, the measurement of D-3-Hydroxybutyrate as well as the blood glucose is needed for the assessment of the severity of diabetic coma and is essential for the exclusion of hyperosmolar non-ketotic diabetic coma. Moreover, the insulin requirements are often based on the extent of the existing hyperketonemia shown by the blood levels of D-3-Hydroxybutyrate is therefore extremely important.
PRECISION
|
Intra assay precision |
||
|
N=10 |
Mean(mmol/L) |
CV(%) |
|
Level1 |
(0.24-0.32) |
<3.8% |
|
Level 2 |
(0.96-1.30) |
<2.5% |
|
Intra assay precision |
||
|
N=80 |
Mean(mmol/L) |
CV(%) |
|
Level1 |
(0.24-0.32) |
<5.0% |
|
Level 2 |
(0.96-1.30) |
<4.5% |
Sensitivity
The absorbance change rate of 1mmol/l samples should be more than 0.0150.
Correlation
The correlation of a well-known brand(X) and Gcell(Y) is y = 1.0607x - 0.014, R2 = 0.9998

Interference
|
Analytes |
Concentration |
|
Bilirubin |
20 mg/dl |
|
Hemoglobin |
200 mg/dl |
|
Intralipid |
900 mg/dl |
|
ascorbic acid |
20 mg/dL |
|
UA |
15mg/d |
Linearity
In the range of [0.2, 4.5] mmol/L, the correlation coefficient r ≥ 0.99, in the range of [0.2, 1.5] mmol/L , the deviation should not be more than ±0.15 mmol/L; in the range of (1.5, 4.5] mmol/L, the deviation should not be more than ±10%.