Heart-type Fatty Acid-Binding Protein
H-FABP
Method: Latex Immunoturbidimetric Liquid reagent: R1: R2=4:1
CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE
Fatty acid-binding proteins (FABP) are a class of cytoplasmic proteins that bind long chain fatty acids. FABP are small intracellular proteins (~13-14 kDa) with a high degree of tissue specificity. They are abundantly present in various cell types and play an important role in the intracellular utilization of fatty acids, transport and metabolism. There are at least nine distinct types of FABP, each showing a specific pattern of tissue expression. Due to its small size, FABP leaks rapidly out of ischemically damaged necrotic cells leading to a rise in serum levels. Ischemically damaged tissues are characterized histologically by absence (or low presence) of FABP facilitating recognition of such areas. Following acute myocardial infarction (AMI) the small protein H-FABP is rapidly released into the circulation. So H-FABP is a sensitive new AMI marker.
PRECISION
|
Inter assay precision |
|||
|
N=5 |
Batch 1 |
Batch 2 |
Batch 3 |
|
Mean |
17.77 |
17.62 |
17.82 |
|

|
17.74 |
||
|
(Xmax-Xmin)/ |
(17.82-17.62)/17.74*100=1.12% |
||
|
Intra assay precision |
|||
|
N=20 |
Level 1 |
Level 2 |
Level 3 |
|
Mean (ng/ml) |
5.38 |
17.62 |
30.47 |
|
SD |
0.24 |
0.25 |
0.20 |
|
CV |
4.46% |
1.42% |
0.66% |
SENSITIVITY
When the sample concentration is 20 ng/ml, the rate of change in absorbance should be greater than 0.0100.
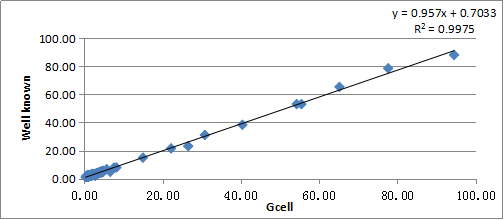
CORRELATION
The correlation of a well-known brand(Y) and Gcell(X) is y = 0.957x + 0.7033, R2 = 0.9975.
|
Analytes |
Concentration |
|
Bilirubin |
50 mg/dl |
|
Hemoglobin |
500 mg/dl |
|
Intralipid |
600 mg/dl |
|
RF |
380IU/ml |
LINEARITY
Linearity is [2.5,130]ng/ml