α1-Microglobulin
AMG
Method: Latex Immunoturbidimetric Liquid reagent: R1: R2=1:1
CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE
α1-Microglobulin (α1-MG) is a low molecular weight glycoprotein for approximately 24,000 to 33,000 Daltons. α1-MG was originally isolated from the urine of patients with renal tubular disease in 1975. It is mainly synthesized by the liver and widely distributed in various body fluids.
Except for a few liver diseases that cause changes in α1-MG in the blood, other diseases such as rheumatoid and tumor do not cause changes in α1-MG. Α1-MG is reabsorbed in the renal tubules after passing through the glomerulus, so its urine concentration change may reflect impairment of glomerular or (and) renal tubular function.
The detection of α1-microglobulin in serum and urine is of great significance for the diagnosis, assessment of progress and prognosis of renal disease.
PRECISION
|
Intra assay precision |
||
|
Sample (Serum) |
Concentration level (mg/L) |
CV |
|
Control 1 |
17.1 |
< 3 % |
|
Control 2 |
34.3 |
< 3 % |
Inter assay precision
Sample (serum)
Concentration Level (mg/L)
CV
Control 1
17.1
< 3%
Control 2
34.3
< 3 %
SENSITIVITY
when the serum sample concentration is 17.1 mg / L, its absorbance change should be less than 0.0100.
3.2 When the urine sample concentration is 3.4mg / L, its absorbance change should be less than 0.0080.
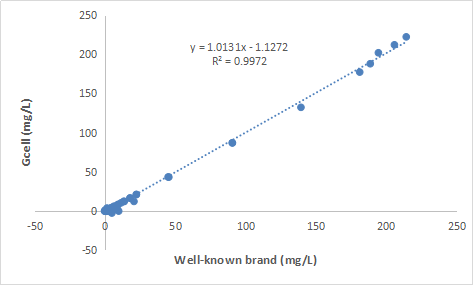
CORRELATION
The correlation of a well-known brand(X) and Gcell(Y) is y = 1.0131x - 1.1272,R2 = 0.9972.
|
Analytes |
Concentration |
|
RF |
400IU/ml |
|
VC |
60mg/dl |
|
Intralipid |
1000mg/dl |
|
DB |
60mg/dl |
|
HB |
500mg/d |
LINEARITY
Linearity is [3.0, 137.0] mg/L.
