Method: FAPGG Substrate Method Liquid, Single reagent
CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE
Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE), also known as kininase II, is a dipeptidyl carboxypeptidase (EC 3.4.15.1) with a molecular weight of at least 129,000. The structure of this glycoprotein shows a single polypeptide chain, a polysaccharide residue and a zinc atom. ACE is present in many different cell types such as neuronal cells and renal proximal tubular cells, but is mostly found in endothelial cells. It is attached to the endothelial surface membrane by an anchor peptide and can be cleaved to be released into the blood circulation as soluble enzyme. Serum ACE activity issignificantly elevated in patients with untreated active disease. Spontaneous orcorticosteroid-induced remission of sarcoidosis is indicated by decreasing serum ACE values. Only few patients with lung diseases such as tuberculosis, fibrosis and tumors, show elevated serum ACE values. Measurement of serum ACE activity is therefore extremely useful as an aid in the diagnosis and in the management of sarcoidosis. The determination of ACE activity in Gaucher's disease is not used as a screening procedure, but its value is significantly increased in most cases if sarcoidosis can be excluded6.ACE is inhibited by drugs from the family of Captopril. Agents acting through this mechanism are now well established inthe treatment of heart failure and hypertension. Serum ACE activity can be a useful parameter for monitoring the effectof these hypotensive drugs inhibiting ACE.
PRECISION
|
Intra assay precision
|
|
N=20
|
level 1
|
level 2
|
|
Mean(U/L)
|
43.93
|
111.33
|
|
SD
|
1.8
|
1.14
|
|
CV(%)
|
4.10
|
1.03
|
Sensitivity
|
LOB
|
1.2U/L
|
|
LOD
|
6.8U/L
|
|
LOQ
|
10U/L
|
|
Mean-3*SD
|
5.9U/L
|
Correlation
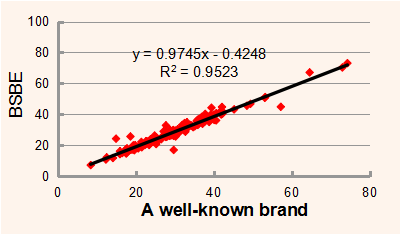
The correlation of a well-known brand(X) and Gcell(Y) is y = 0.9745x - 0.4248 R2 = 0.9523
Interference
|
Analytes
|
Concentration
|
|
Bilirubin
|
25μM
|
|
Hemoglobin
|
25mg/dl
|
|
TG
|
450mg/dl
|
Linearity
Linearity is 10-150 U/L.